OMEGA-3: ITS INVOLVEMENT IN STRESS AND SLEEP
Since 2020, stress and sleep disorders have been increasingly concerning the consumers. The market for dietary supplements focused on these issues is experiencing strong growth in Europe, with popular ingredients such as valerian, melatonin, and B-group vitamins.
However, omega-3s are emerging as a new opportunity to enhance mental well-being. Their beneficial effect on the nervous system makes them promise an ingredient for anti-stress and sleep formulations.
In this article, you’ll discover the possibilities offered by these omega-3s
STRESS AND SLEEP: A HEALTHY MARKET
Consumers looking for anti-stress solutions
Since 2020 and the Covid-19 pandemic, the French have faced more stress and sleep problems. In fact, following the anxiety-inducing context of the pandemic, 53% of French people said that the health situation increased their stress levels and 42% said sleep was impaired, according to a study conducted by Harris Interactive. Overall, more than a third of the total population is affected by a sleeping disorder! [1]
Stress and sleep: the flagship segments in nutraceuticals
The stress and sleep segments represent a significant proportion of food supplements in France. These segments continue to grow with sales increasing by more than 12.1% in pharmacies, 14.1% in parapharmacy outlets and 5.3% in supermarkets and hypermarkets in 2021! [2]
According to Clear Cut Analysis, sales of dietary supplements to combat stress increased by 31% between 2020 and 2021 and sales of supplements to improve sleep more than doubled (55%). [3]
The key stress-sleep ingredients

In phytotherapy, plants such as valerian, eschscholtzia (California poppy) and passiflora are widely used in dietary supplements to combat stress and sleep disorders. The key active ingredient for improving sleep is melatonin, a molecule naturally produced by the body at bedtime. In 2021, the global melatonin market was worth $1.26 billion. [4]
To combat stress and improve sleep, tryptophan in the form of 5-HTP is increasingly found in dietary supplements. This essential amino acid is a precursor to melatonin but also to serotonin, nicknamed the “happiness hormone” and strongly involved in regulating stress. [1]
Finally, as for vitamins and minerals, vitamins from group B (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B8, B9, B12) and magnesium are among the active ingredients commonly used to reduce stress and improve sleep. These molecules contribute to serotonin synthesis.
Omega-3 oils are active ingredients that are still rarely used to treat sleep disorders and combat stress, however, their benefits are increasingly being studied and we will come to rely on them increasingly in coming years.
OMEGA-3: A NEW INGREDIENT FOR YOUR STRESS-SLEEP FORMULATIONS
The physiology of sleep
Sleep is characterized by a sequence of 3 to 6 successive cycles ranging from 60 to 120 minutes each. Each cycle is itself composed of a phase of slow sleep and REM sleep.
These different phases are highly variable during the night, with the first cycles consisting more of slow, deeper sleep, with more cycles of REM sleep at the end of the night. They also depend on the quality of previous nights, age and lifestyle.
Sleep, that we believe is simple, is actually the result of a series of chemical reactions. However, it would appear that adenosine, produced massively when we are awake, plays an important role in falling asleep by gradually inhibiting brain function.
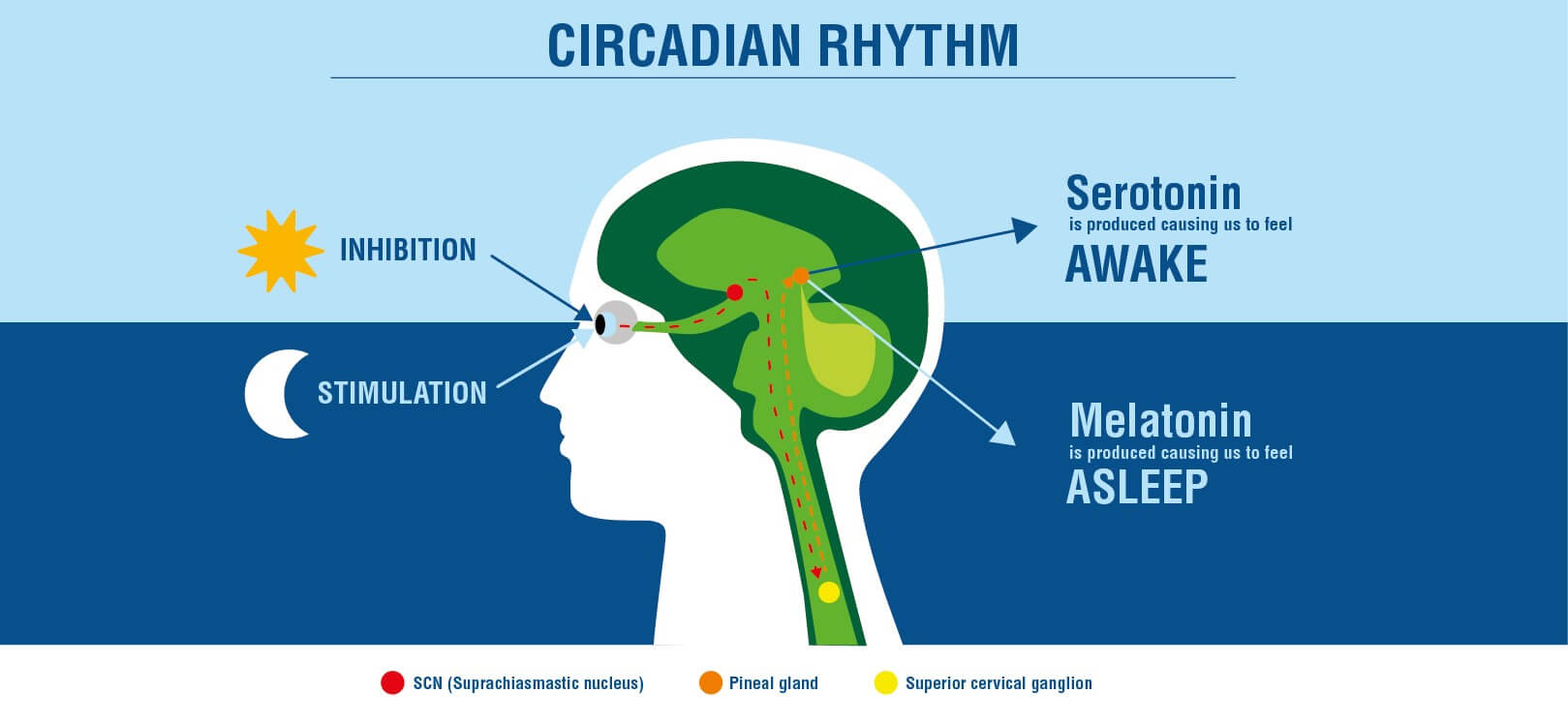
Melatonin, nicknamed the sleep hormone, also contributes to triggering it. It is produced when the body is plunged into darkness, thanks to the pineal gland, located at the back of the hypothalamus. Its production decreases with age, leading to sleep disorders.
Finally, many genes, called clock genes, whose expression is modulated by several factors (melatonin, retinal cells, etc.) help regulate sleep and the circadian cycle. [5]
Circadian Rythm
The physiology of stress
Stress is a normal physiological mechanism necessary for our survival. It corresponds to all the body’s responses to a potentially dangerous or unknown situation. Nowadays, we no longer face the same threats, but the physiological reactions remain the same. [6]
When a stress factor is perceived by the body, a cascade of reactions occurs. In fact, several areas of the brain are activated such as the amygdala, prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Activation of the amygdala leads to the release of neurotransmitters (chemical molecules) such as dopamine or noradrenaline, which allow the body to be in a state of hypervigilance in response to the stressful factor. Other neurotransmitters are in turn released into the blood and enable the release of glucocorticoids including cortisol, considered as the stress hormone. [7]
These hormones lead to biological changes: increase in vascular tone, heart rate or blood pressure. They also make it possible to mobilize the whole body in response to stress by inhibiting metabolic functions such as digestion or reproduction.
Once stress has passed, stress hormones act on the brain to suppress and memorize the response to stress. [7]
The relationship between sleep and stress
Stress and sleep are intimately linked. A survey by the Institut du Sommeil et de la Vigilance in 2018 revealed that only 55% of people who say they are stressed are satisfied with their sleep. [8]
Stress affects the different stages of sleep by making it difficult to fall asleep and producing night awakenings. A vicious circle then sets in as disturbed sleep over several nights becomes an additional stress factor. [9]
When stress becomes chronic or too intense, the recovery of the body is disrupted and harmful effects are felt. In the long term, diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease or psychological disorders (anxiety, depression, etc.) may occur. [7]
The anti-stress effect of omega-3
The benefits of omega-3 on the body have been recognized for many years. More recently, it is its actions on the nervous system that have interested researchers.
Omega-3 increases endocannabinoid production which plays a role in stress resistance. Several studies in mice have shown that low omega-3 consumption reduced their endocannabinoid production and increased their stress. [10]
Other studies have shown the role of omega-3 on the effect of cortisol, the stress hormone. Continued exposure to high levels of cortisol increases the inflammatory response. The anti-inflammatory effect of omega-3 helps to regulate this inflammatory response and therefore reduces the body’s stress. [11]
The study by Hellhammer et al. showed the beneficial effect of omega-3 on chronic and acute stress. For 12 weeks, 2 groups of men aged 30 to 60 took either 300 mg of omega-3 + phosphatidylserine (PS) or an olive oil-based placebo. After 12 weeks of treatment, their stress level was measured by two tests revealing that the group that consumed omega-3 + PS had a response to regulated stress. [12]
Finally, omega-3 helps fight depression by playing on different neurobiological functions. Indeed, omega-3 has been shown to act on the modulation of certain neurotransmitters or neuroplasticity and synaptic plasticity. [13]
The impact of omega-3 on sleep
The brain is the 2nd most lipid-rich tissue (50%) [14] whose neuron membranes are characterized by the presence of specific fatty acids such as omega oils and phospholipids. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is the most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in the brain.
A sufficient supply of omega-3 therefore contributes to normal brain function. For more information, see our article on mental well-being.
The effect of omega-3 on sleep was demonstrated in a study of children in England. Researchers from the Oxford team carried out a double-blind study on children aged 7 to 9. One group consumed 600 mg of omega-3 (mainly with DHA) daily for 4 months and the other group took a placebo. Children who received the omega-3 supplement slept an average of 58 minutes more per night. This improvement would be due to a higher concentration of DHA in the blood according to the authors. [15]
Although it is necessary to carry out additional studies on a larger number of children, the omega-3 pathway appears promising to improve the quality of sleep.
Omega-3 opportunities in the stress and sleep sphere
Stress and sleep disorders are more relevant than ever and can affect the entire population. Moreover, the stress-sleep segment represents nearly 20% of the European nutraceuticals market in value. In this mature and highly competitive market, the challenge for brands is to stand out with innovative formulas. Today, omega-3 is a lever for innovation, especially if you opt for omega-3 of plant origin to meet consumers’ natural expectations.
This is why DHA ORIGINS® by Fermentalg is an optimal solution for your stress-sleep formulations. Derived from the fermentation of the Schizochytrium sp. microalgae, DHA ORIGINS® is naturally concentrated in vegan omega-3 (with a minimum of 550 mg/g DHA in the form of fatty acids).
SOURCES
[2]https://www.synadiet.org/sites/default/files/news/files/202111060_harris_interactive_rapport_barometre_conso_cpal_2022_v_ag_synadiet.pdf
[3]https://nutraceuticalbusinessreview.com/news/article_page/Stress_and_sleep_supplements_more_than_a_fleeting_post-pandemic_trend/205384
[4]https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/melatonin-market/
[5]https://www.inserm.fr/dossier/sommeil/
[6]https://www.frcneurodon.org/comprendre-le-cerveau/a-la-decouverte-du-cerveau/le-stress/
[7]Marie-Pierre Moisan, Michel Le Moal. Le stress dans tous ses états. Med Sci (Paris). 2012 June; 28(6-7): 612–617. Published online 2012 July 16. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2012286014
[9]https://institut-sommeil-vigilance.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/INSV-Carnet-3-Sommeil-Stress-2020.pdf
[10]Lafourcade, M., Larrieu, T., Mato, S. et al. Nutritional omega-3 deficiency abolishes endocannabinoid-mediated neuronal functions. Nat Neurosci 14, 345–350 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2736
[11]Thesing CS, Bot M, Milaneschi Y, Giltay EJ, Penninx BW. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid levels and dysregulations in biological stress systems. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Nov 1;97:206-15
[12]Hellhammer, J., Hero, T., Franz, N., Contreras, C., & Schubert, M. (2012). Omega-3 fatty acids administered in phosphatidylserine improved certain aspects of high chronic stress in men. Nutrition research, 32(4), 241-250.
[13]Zhou Lie, Xiong Jia-Yao et al., Possible antidepressant mechanisms of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids acting on the central nervous system. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.933704
[14]https://alwaysomega3s.com/why/brain-health
[15]Montgomery, P., Burton, J.R., Sewell, R.P., Spreckelsen, T.F. and Richardson, A.J. (2014), Fatty acids and sleep in UK children: subjective and pilot objective sleep results from the DOLAB study – a randomized controlled trial. J Sleep Res, 23: 364-388. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12135